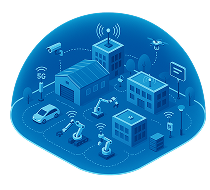
Private 5G refers to a locally managed, on-premise 5G network built entirely for the use of a single organization within their properties like factories, warehouses, campuses and more.
Rather than relying on public carriers, a private 5G network gives an enterprise direct control through their own equipment and private, shared, or lightly-regulated spectrum.
It opens up possibilities like deploying mission-critical communications for applications such as asset tracking, automated logistics, mobile workforces and Industrial IoT. Private 5G can support these situations with high-speed connectivity, low latency and strong security in environments not feasible with WiFi.
Facilities set up dedicated antennas and radio infrastructure to enable private 5G throughout indoor and outdoor spaces. Network management is handled on-site so mission-critical communications are isolated from public networks. Some organizations even install their own LTE core elements for additional oversight.
As private 5G becomes more popular with larger installations, new business opportunities are arising. Telecom vendors now offer turnkey private 5G network packages. Managed service providers handle installation and 24/7 monitoring.
For the right scenarios, private 5G brings the speed, reliability and control necessary for digitally transforming industrial operations. Its growing role complements both the wifi and macro cellular networks that power our everyday connectivity experiences.
How do Private 5G Deployments work?
Behind the Scenes of a Private Cellular Network
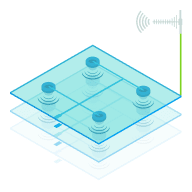
For the end user, connecting to a private network is as simple as replacing a SIM or even downloading an ESIM. But behind the scenes lies a full network infrastructure making private network connectivity possible. For private 5G deployments the key infrastructure components include spectrum licensing, radio access equipment and the core network control plane.
First, the network operator must obtain dedicated spectrum licenses for the desired coverage areas, whether campus-wide or within a single building. This allows legal operation of the customized network without interfering with public cellular bands.
In the US, this is done over CBRS, a shared 150MHz spectrum block in the 3.5GHz band. CBRS offers a good balance of wide bandwidth and indoor/outdoor propagation properties. The FCC has opened up this spectrum for commercial cellular and WiFi use. CBRS spectrum uses a three-tier Spectrum Access System to manage sharing between users. Priority access licenses are available to carriers, general authorized access is for shared commercial/enterprise use, and incumbent access is reserved for government radar.
Next comes deployment of the radio layer. Small cells provide coverage across buildings/campuses. More rarely, Distributed Antenna Systems can ensure in-building propagation too. Base stations wirelessly connect to user devices using the licensed frequencies.
An Evolved Packet Core (EPC) acts as the private network's brain. Managing authentication, connectivity sessions, firewalls and more, the EPC ensures only approved devices and applications can access the network resources.
With all these factors operational, private 5G brings standardized 5G connectivity to facilities under a single operator's control.
Ongoing management includes monitoring network usage, maintaining equipment and making capacity upgrades or expansions as needs evolve over time. Remote troubleshooting tools also keep private 5G networks running optimally.
Key benefits of a Private 5G deployment
- Dedicated spectrum and network - Private 5G uses licensed unused spectrum, allowing organizations to have their own private wireless network independent of commercial carriers. This ensures reliable, secure connectivity.
- Improved coverage - Private 5G can provide consistent indoor and outdoor coverage across large campus/facility footprints using small cells. This includes hard-to-reach areas like basements, parking lots etc.
- Enhanced reliability - The private network architecture makes Private 5G deployments highly reliable compared to commercial networks which can experience congestion.
- Deterministic low latency - Latency is kept extremely low and consistent for mission-critical applications through real-time networking capabilities.
- Futureproof technology - Private 5G uses 5G standards, futureproofing the wireless infrastructure for the next decade.
- IoT enablement - It opens the door to mass IoT/M2M deployment for sensors, machines etc through network slicing and dedicated core functionality.
- Cost savings - Operational expenditures are lower than maintaining separate WiFi and cellular networks due to converged connectivity on one network.
- Control and customization - Operators have full control and flexibility to customize the network as per their unique requirements.
Can Private 5G help your facility?
Private 5G technology is suitable for any commercial facility, from warehouses to hospitals, universities, and shopping malls. Whereas traditional Wi-Fi might struggle with scale and meeting connectivity SLAs, and public cellular fails to offer control or flexibility, private cellular seamlessly bridges the gap, providing a robust "wide-area LAN" that's tailored to any organization's precise needs.
- Offices
- Schools & colleges
- Warehouses
- Manufacturing facilities
- Hotels & venues
- Healthcare & hospitals
- Shipping ports
- Utilities
- Oil, gas, and mines
- Luxury homes

As CEO and cofounder of Waveform, Sina has been helping people boost their signal since 2006. He has personally tested and installed hundreds of signal boosters.
He welcomes feedback via Twitter, LinkedIn, or by email to [email protected].